Want to familiarize yourself with MCAT eye anatomy content? Below, we’ll cover everything you should study: the functions, diagram, and photoreceptor comparison. Also be encouraged to check out our overview of all MCAT biology and biochemistry topics.
Plus, click the link below for a handy PDF version of this overview, and for many other MCAT resources!
The Human Eye: Structure and Function
| Structure | Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Outermost lens of the eye responsible for the majority of light refraction |
| Aqueous humor | Fluid that adds refractive power |
| Iris/Pupil | Colored tissue that regulates the amount of light entering the eye through the central pupil
*KEY CONCEPT: The pupil dilates in low light conditions and constricts in high light conditions |
| Lens | Focuses light, bends to allow accommodation
*KEY CONCEPT: Accommodation: altering the lens so the eye can focus on both near and far objects |
| Ciliary Body | Changes shape of lens during accommodation |
| Vitreous Humor | Jelly-like substance that fills the inner eye |
| Sclera | Tough outer coat for protection and muscle attachment |
| Retina | Light sensitive layer over the back of the eye containing photoreceptors |
| Macula/Fovea | Area of the retina with high visual activity due to high concentration of cones |
| Optic nerve | Carries information from the retina to the occipital lobe of the brain. The blind spot is where the nerve exits the eye. |
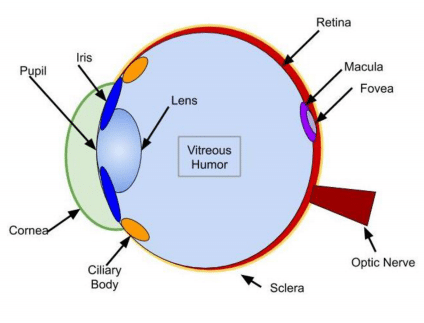
MCAT Eye Anatomy: Diagram of the Human Eye
Light refracts (bends) as it passes sequentially through the cornea, aqueous humor, lens, and vitreous humor. Errors in refraction cause visual defects which can be corrected by contacts or glasses. Myopia and hyperopia are two types of refractive error.
Here is a basic diagram of the human eye, so you can get a sense of this process:
Comparison of Photoreceptors
| Rods | Cones | |
|---|---|---|
| Used For | Night vision, low resolution | Day vision, high resolution |
| Primary Location | Periphery of retina | Central retina: macula and fovea |
| Relative Number | More | Fewer |
| Colors Perceived | None | Red, blue, green |
MCAT Eye Anatomy: A Final Word
As always, the goal of studying isn’t just memorization. Rather than trying to cram all of the human eye structures and functions into your mind, focus on how these parts work together to create the phenomenon of vision!
If you’d like more MCAT eye anatomy practice, we highly encourage you to check out Magoosh’s MCAT prep. It includes 380 lessons, 745+ practice questions, personalized email assistance, and more! Happy studying and good luck on the MCAT!






