
Five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, fighting ceased. Then, World War I was over with the signing of the Treaty of Versailles. Here are some Treaty of Versailles APUSH review facts you should know for the exam.
What Is the Treaty of Versailles?
The Treaty of Versailles marked the end of World War I. Incidentally, politicians from various countries met in the Versailles Palace to discuss the particulars of the treaty. It was negotiated by the Allied Powers with very little participation from Germany. France wanted to take a harsher stand with Germany including splitting up Germany to prevent future wars.
U.S. President Woodrow Wilson offered Fourteen Points that he believed should be considered. For example, he advocated for the creation of the League of Nations to resolve international disputes.
The Treaty of Versailles consisted of 15 parts with 440 articles. It stripped Germany of their Army, Navy, and Airforce; prohibited Germany to create or possess certain types of weapons; reassigned Germany borders; and made Germany liable for billions of dollars of reparations under the War Guilt Clause.
Years
Negotiated between January and June 1919
Signed: June 28, 1919
Why Is It Important?
Historians believe that the terms of the Treaty of Versailles led to Hitler’s rise of power. Consequently, it also led to World War II and the Holocaust.
Although the treaty was more lenient than France wanted, the terms were harsh for Germany. This laid the groundwork for the rise of the Nazi Party.
People
- Henry Cabot Lodge- A republican senator who fought against the ratification of the treaty. He was the leader of the reservationists, who pledged to vote in favor of the treaty if certain changes occurred.
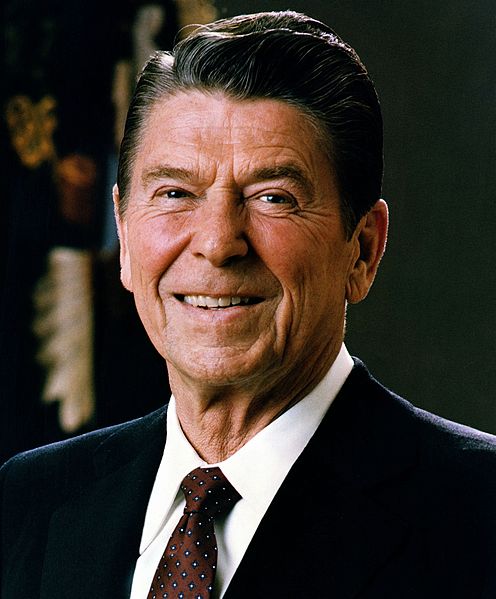
- Woodrow Wilson- President of the United States during World War I. He delivered a speech in January 1919 outlining Fourteen Points. Some of these points included the ending of the war, creation of a peacekeeping organization, disarmament, free trade throughout Europe, and the spreading of peace and democracy.
- Georges Clemenceau- The French Prime Minster during World War I.
- Charles Delandier- The French representative sent to negotiate the terms of the Treaty of Versailles.
- David Lloyd George- The British Prime Minister during World War I. He served as the middle man between France and American during negotiations for the treaty. He wanted harsh punishments for Germany, but he hoped to keep Germany strong to help fight Russia if the Russian Revolution spread throughout Europe.
- Irreconcilables- A group of Republicans and Democrats who opposed the Treaty of Versailles. They didn’t agree with the clause that members of the League of Nations would have to go to war for their allies. They were isolationists, choosing to stay out of conflicts around the world. Also, they felt that this took away Congress’ power to declare war. Because of these issues, the U.S. never became a member of the League of Nations.
- League of Nations- An organization created by the Paris Peace Conference. It was an international peacekeeping organization that worked to resolve international disputes peacefully. The idea for this organization originated from Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points. However, the U.S. never joined the League of Nations.
Treaty of Versailles APUSH Practice Question 1
1. The U.S. chose not to sign the Treaty of Versailles, because:
a. Germany wasn’t held accountable for initiating the war with the Allied countries.
b. joining the League of Nations became an obligation for countries that signed.
c. it failed to create a peacekeeping organization to prevent future international disputes.
d. President Wilson urged Congress to stay out of foreign affairs.
Answer: B. Article X stated that the nations who signed the treaty would automatically join the League of Nations. Several members of Congress spoke out against this. Since countries in the League of Nations had to agree to help other nations at times of war. They felt that this took away their power to declare war, and they didn’t want to get involved in wars unnecessarily.
Treaty of Versailles APUSH Practice Question 2
2. The Treaty of Versailles included all the following EXCEPT:
a. The requirement of setting up a democracy.
b. The creation of the League of Nations.
c. The assigning of war guilt to Germany.
d. The amount of reparations Germany needed to pay.
Answer: A. In the 15 parts of the Treaty of Versailles, it outlines the creation of the League of nations, made Germany liable, and required Germans to pay war reparations. Although Woodrow Wilson discussed spreading democracy, the Treaty of Versailles did not require democracy to sign.
Treaty of Versailles APUSH Practice Question 3
3. Which of the following was NOT one of President Wilson’s Fourteen Points?
a. A call to reduce military forces and weapons in Europe.
b. The creation of an international peacekeeping organization.
c. The War Guilt Clause to hold Germany liable for the war.
d. The end of fighting during World War I.
Answer: C. Although the War Guilt Clause was included in the Treaty of Versailles, it was not in Woodrow Wilson’s Fourteen Points. America wanted to be more lenient with Germany than France wanted. Today, people believe that the War Guilt Clause opened the door for Hitler’s regime.
Treaty of Versailles APUSH Practice Question 4
4. What was President Woodrow Wilson’s goal at the Paris Peace Conference?
a. He wanted to create what was to become the League of Nations.
b. President Wilson hoped to end communism throughout Europe.
c. He hoped to hold Germany accountable for killing American soldiers.
d. President Wilson needed reparations to help pay off war debts.
Answer: A. Creating a peacekeeping organization was something that President Wilson really wanted to do. Consequently, he discussed this idea as part of his speech at the conference. He hoped that this organization could peacefully handle international conflicts without the need for military combat.
How did you do with the Treaty of Versailles APUSH practice questions? In any case, think about how the Treaty of Versailles led to World War II as you consider themes for the exam. Happy studying!




Leave a Reply