
Curious about the enzyme kinetics MCAT content you’ll find on the Bio/Biochem section? We’ve got you covered! Below is a quick overview of MCAT enzymes to know as well as enzyme classification, features, regulation, and more. Also check out this guide to the most common MCAT topics you’ll find on the test as well as this guide to the bio and biochem section of the MCAT.
For a handy PDF version of this material, as well as more great MCAT resources, click the link below!
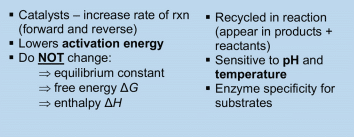
MCAT Enzymes Features
Here are some key enzyme features:
Cofactors and Coenzymes
Their purpose is to improve enzymatic function.
Cofactors: inorganic molecules, metals ions (Zn+2, Cu+2, Fe3+)
Coenzymes: small, organic, vitamin derivatives (NAD+, FAD, coenzyme A)
Examples:
- Apoenzymes
- Holoenzymes
- Prosthetic groups
Six Enzyme Classifications
Here’s a breakdown of enzyme classification:

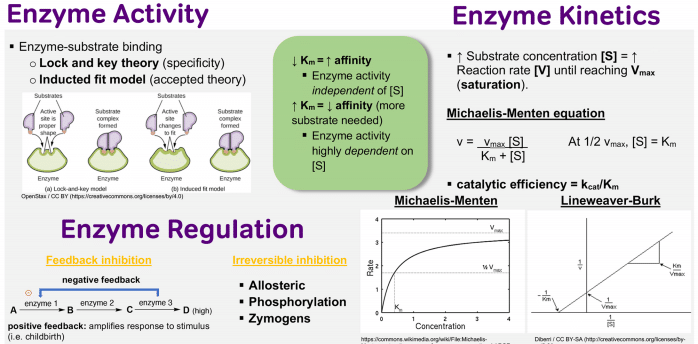
Enzyme Activity, Enzyme Kinetics, and Enzyme Regulation
Enzyme kinetics MCAT content can feel a little daunting, so we’ve broken down how activity, kinetics, and regulation are all related below:
Enzyme Regulation: Reversible Inhibition
| Competitive | Noncompetitive | Mixed | Uncompetitive | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binding Site | Active site | Allosteric site | Allosteric site | Allosteric site |
| Impact on Km | Increases | Unchanged | Increases or decreases | Decreases |
| Impact on Km | Unchanged | Decreases | Decreases | Decreases |
A Final Word on MCAT Enzymes Questions
Enzyme content can feel overwhelming as you’re studying, but the key to understanding their more complex activity and regulation lies in first grasping their features and functions. And when you understand the mechanics of enzyme kinetics, you’ll be better able to memorize the Michaelis–Menten equation. Remember, succeeding on this section requires more than just formula memorization.
Happy studying and good luck!







Leave a Reply